What is Botox Injection? Ultimate Guide
What is Botox?
Botox Danger Zones, The word Botox stands for botulinum toxin type A, secreted by a bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It is a neurotoxin that suppresses the function of acetylcholine and relaxes the muscles.
Botox is an injection that people use to reduce wrinkles, look younger, and look thinner. When it is injected, the facial muscles that cause wrinkles get temporarily paralyzed due to the blockage of nerve impulses. This article will help you to understand What is botox? How does botox work? What are botox danger zones? Benefits of botox injection, and Is botox helpful for skin care?
Areas for Botox injection
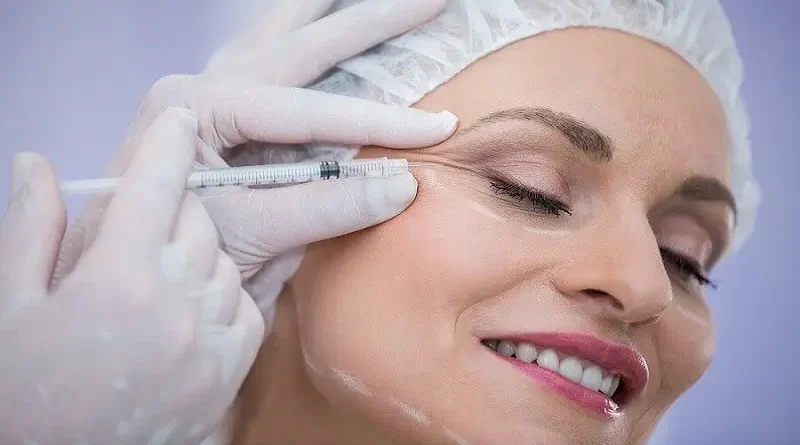
It is injected with micro-needle in those areas which are more requested. The most beneficial and requested areas for treatment are the facial muscles like orbicularis oculi, frontalis, and procerus around the eyes, forehead, and between the eyebrows that cause wrinkles. 1- 3 injections are given in the required areas.
The best age for Botox treatment
It can be started at the age of 18 and onward, but experts say that the 20s and 30s are the best age for preventive Botox treatment. Our skin contains several substances, especially protein which keep our skin fresh and young. Collagen, Elastin, and hyaluronic acid are significant substances that play an important role in keeping our skin smooth, fresh, and tight. Collagen prevents our skin from harmful elements in the environment like the sun.
Elastin is also an essential protein that provides elasticity to our skin, and hyaluronic acid plays a critical role in moisturizing our skin and maintaining the hydration level. The production of these substances is very high when we are young, so our skin looks fresh, wrinkle-free, hydrated, and smooth. Still, with time when we get older, our skin produces less quantity of these substances, and as a result, memorable lines and wrinkles become prominent. Botox toxin is used to eliminate these undesired wrinkles and fine lines.
Benefits of Botox treatment
After getting Botox treatment, you will see excellent results because this treatment works very deeply within the skin and protects us from the formation of wrinkles and fine lines on the face. Anti-ageing products are available on the market, but those products provide minimal effect; on the other hand, Botox treatment is more effective because it works very deeply, and its results are long-lasting, from four to six months.
Patients can enjoy smooth, hydrated, and elastic skin after Botox treatment, and only two-four sessions are required each year.
People who should not use this treatment
The Botox treatment is safe for use and approved by FDA. Still, people with allergic problems, diabetes, eye disorder like glaucoma, muscle and nerve disorder, and bleeding problems cannot enjoy this treatment. Pregnant and breastfeeding women also cannot use it.
Side effects of Botox
The symptoms that can be seen in this treatment are as follows.
Those people who use this treatment cannot easily swallow the food. They feel body pain in specific areas like the Neck, Head, Legs, and back. In which areas Botox has been injected, the sweating rate increases compared to underarm. Temporarily weakness or paralysis occurs of nearby musculature due to this treatment.
Precautions and instructions for Botox Injection
Cosmetic surgeons or nurses advise the patient not to massage and rub his face after getting a Botox injection. The patient is also suggested not to perform any exercise and not to use any medication at the injected sites.
Is Botox treatment painful?
Botox treatment is given with microneedles, and this procedure is speedy. If we use numbing cream, then Botox treatment is painless, and this procedure is slightly painful without numbing cream.
How do Botox Danger Zones Calculate?
When Botox is injected, it blocks the releasing site and effects of acetylcholine, which presynaptic motor neurons and muscles relax. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that contracts the muscle and loses its function under the influence of toxins.
Botox Danger Zones
Nowadays, facial filler injections are becoming more popular than surgical rejuvenation of the face for immediate results, so Botox injection is expected out of several facial filler injections. The injection is given by an experienced healthcare professional who knows the anatomy and danger zones of the face, keeps in mind the vasculature’s depth and location, and uses unique techniques to prevent vessel injury within each zone. There are 6 botox danger zones in the face, namely,
- Glabella
- Temple
- Infraorbital Region
- Perioral area ( lips)
- Nasolabial Fold
- NOSE Region
Glabella Region
In this zone, the supraorbital and supratrochlear arteries are initially deep, and then about an inch above the foramen, they become superficial. So, low G prime filler is used in this region, and to prevent the backflow into the orbit, use a finger on the supraorbital rim.
Temple Region
In this zone, the superficial temporal artery and middle temporal vein are avoided to be injected. When injected, the superficial temporal artery was shown to deliver dies into both eyes, so it is imperative to inject at least 2cm above the superior border of the zygoma and posteriorly from the brow’s tail.
Infraorbital Region
The Infraorbital foramen is 11mm below the Infraorbital margin and about an inch from the midline, and Botox is injected laterally, and the product is pushed toward the medial canthus.
Perioral Region (lips)
The superior labial artery passed posteriorly from the mucosa muscle and several millimetres above the inferior border in this region. So the low G prime filler is used in this zone at the vermilion cutaneous border.
Nasolabial fold
The facial artery has a tortuous route along the Nasolabial fold toward the medial angle of the eye. The upper two-thirds of the facial artery is superficial, and the lower two-thirds lie beneath the muscle. The angular artery extends to give off the labial artery, which communicates with the dorsal nasal artery, a direct ophthalmic branch. It is the second most common site to give blindness.
NOSE Region
The dorsal nasal artery direct branch of the ophthalmic artery communicates with all the other components of the facial artery, and the vasculature is shallow within the nose. A misplaced injection in this region can lead to blindness, ocular ischemia, and alar necrosis.